Language is a Progressive House track produced by Porter Robinson which features vocals by Heather Bright. The song was uploaded on YouTube by Porter Robinson on March 30, 2012 and received number 1 in the UK indie charts and number 3 in the UK dance charts.
The track incorporates many tropes from Trance and euro dance such as time signature, structure and instrumentation. I used Phase cancellation within Logic X to compare between different segments so i could pick up different sounds that might be less prominent since the second half of the song is just duplicate of the first.
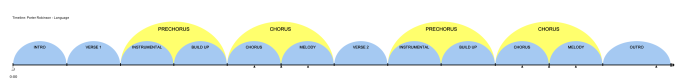
Song Structure
Intro (Bar 1 – 16 , 0:00 – 0:30)
The first segment starts off with a percussion loop with a kick on every 1/4, a snare on every 1/2 and toms in between ever kick and snare. the only exception is in the last bar where the kick is muted leaving the tom and snare to play.
There are also hi-hats which play every 1/4 and a heavily reverbed and delayed crash which decays overtime until the end of the segment. it is also worthy of note that the crash is also sidechained every 1/4 and overtime, the sidechain wetness increases to the point where the last bar without the kick, the crashes provides the overall beat instead of the kick.
In the drum bus itself, there are two notable Fx processing that is being used. The first is Bitcrushing. The percussions such as the toms and kick have a very metallic high end to them and it is almost recreating the very early days of 8 bit music where percussions were made using saw waves and white noise. The second notable Fx is the heavy use of reverb. Certain percussions like the snare uses a smaller reverb with a shorter release and the cymbals use a far more larger Reverb space with a longer release time. The kick, snare and toms are also panned heavily to the centre whereas the hats were panned hard left and right. This gives it an overall vastness and the perception that it is set in a large space but the focal point is the kick, snare and toms since it is in the centre.
Verse 1 (Bar 17 – 32 , 0:30 – 1:00)
The two notable instrumentations in this section are the synth plucks and the heavily reverbed piano in the background.
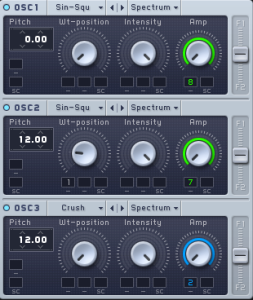
The pluck is a mix of 3 saw waves in unison and detuned to give it a chorus effect. There is a low pass filter being applied to the synth since there is is almost no harsh top end noise that 3 unisoned saw waves create, and it is a much smoother sounding synth with heavy emphasis on the mid and the lows. The envelope for this synth has a fast attack but it has almost no sustain and relies heavily on the decay and release. this gives the synth a plucky sound and would probably be a pad if the sustain was boosted.
There are also piano chords being played in the back which is heavily reverbed to the point where there is almost no dryness to it and most of the sound comes from the wet reverb itself. The reverb release is also very long almost reaching 3-4 seconds.This makes the piano sit well in the far back if the mix whereas the plucks are the main focal point to this section.
There is also a pitched saw lead which rises in the last bar. White noise is also slowly introduced via high pass for the last 4 bars.Both of these create tension for the track to break it up from the calmed section into a more hectic section.
Pre-chorus (Instrumental) (Bar 33 – 48 , 1:00 – 1:30)
In this section a saw wave lead is introduced which in which heavy amounts of distortion is being applied to the overall sound. There is also white noise being applied to the the synth which gives it more energy and grit to the overall sound.
There is also a phased pad which runs in the background which also takes the same synth from the lead but it runs as a whole note chord compared to the broken lead that is being ran in 1/8.
There also seems to be a timestretched lead in the background which almost sounds like a scream. This is the only notable stem with a heavy amount of reverb compared to the saw wave synth which is rather dry and direct.
Pre-chorus (Build Up) (Bar 49 – 64 , 1:30 – 2:00)
In this section the build up incorporates many aspects from the previous section such as the synths and the heavy amount of distortion. However the composition is stripped down and there are new tracks added in
The first notable one is a lead synth with its pitch is being automated using a slow attack envelope. The second is another heavily bit-crushed synth which is being automated using the same setting. these synths recreate the sound of a siren and as the section goes on, more white noise is highpassed into the synths to build up a sense of tension and energy in the track.
Chorus (Bar 65 – 96 , 2:00 – 3:00)
The Chorus is a recreation of the pre-chorus in bars 33-48.
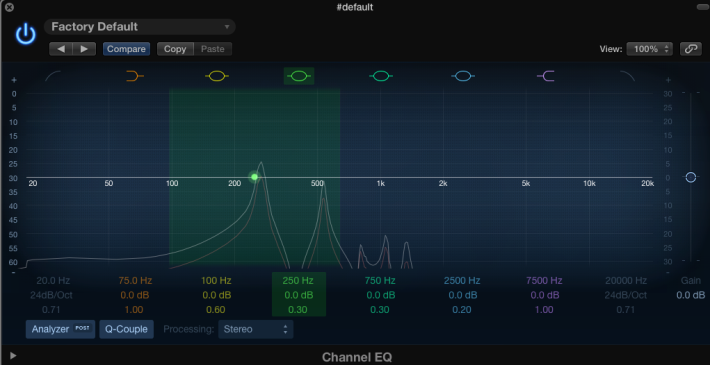
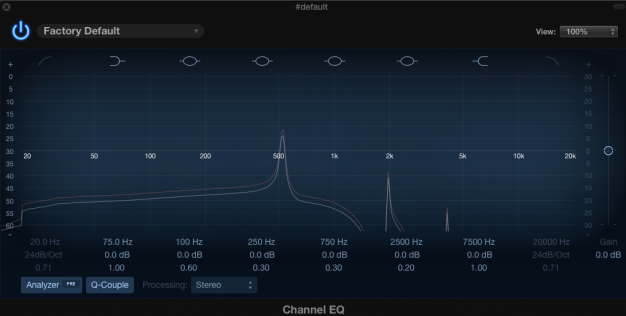
In terms of spectral morphology, there is a noticeable difference towards the low end of 200Hz and below compared to the pre-chorus where it is more dry and missing a lot of its low energy.
The big difference is the 4 to the floor kick that plays during the this section. The kick is a very punchy low end kick with a heavy emphasis towards 40-80Hz.
In terms of synth, the chorus has an addition of a sine-wave sub bass which plays the root note. The overall section is heavily side-chained compressed in terms of dynamic towards the 4/4 kick where as the kick plays, most of the musical contents is ducked down.
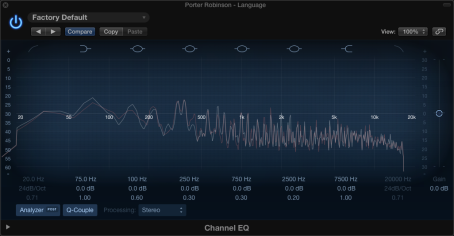
(Pre Chorus Post EQ)
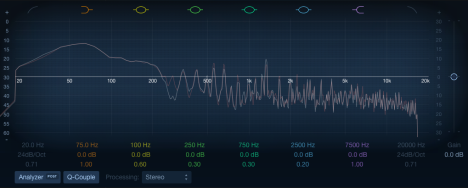
(Chorus Post EQ)
Verse 2 (Vocals) (Bar 97 – 112 , 3:00 – 3:30)
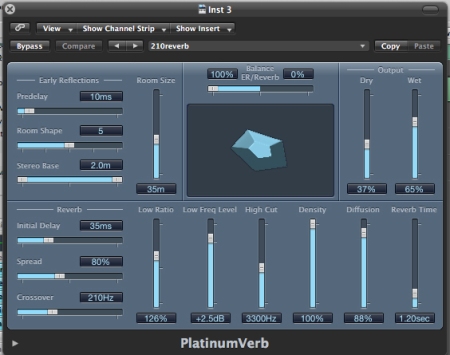
There are female vocals being tracked in this section. In terms of space, there is very little reverb being applied to her voice. This gives the connotation that the vocals are right in front of the listener while most of the music is sitting at the far back. if there was too much reverb, there would not be a centre of focus and the vocals would meld with the overall track.This could also be due to the track aesthetic. for a whole minute during the track there are no human elements to the song and so too much reverb could also be lost within the track. putting too much reverb would lose its more personal touch with the listener since its as if she is in front talking to you rather than an ambient voice in the background.
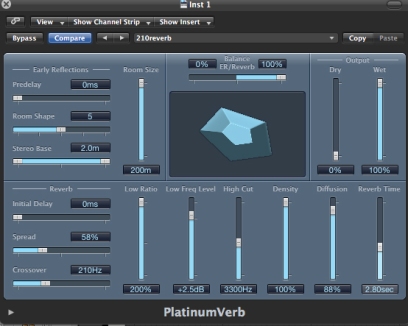
The most interesting part is towards the last bar of the verse, the vocal reverb is actually automated to increase to the point where it merge with the chorus. Ive stated that the in the previous pre-chorus there is a “scream” like sound which could just be the reverb tail dying off and merged to sound like a synth.
Repeated
Pre-chorus (Instrumental) (Bar 113 – 128 , 3:30 – 4:00)
Nothing new added from previous Pre-chorus
Pre-chorus (Build Up) (Bar 129 – 141 , 4:00 – 4:30)
Nothing new added from previous Pre-chorus
Chorus (Bar 145 – 176 , 4:30 – 5:30)
Nothing new added from previous chorus, other than it is stripped in terms of percussion and low end energy in the last 4 bars.
Outro (Bar 177 – 194 , 5:30 – 6:03)
The outro is a duplicate of the intro.




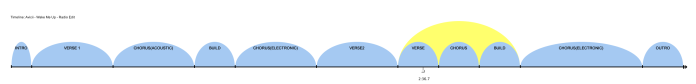
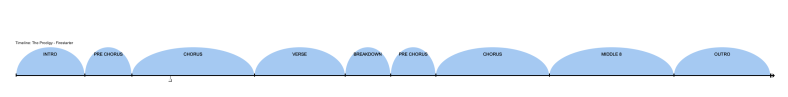 Even looking from the song structure it self, its obvious that it even reflects the whole violent and restless nature of the genre. There is only a 30 seconds interlude, compared to 3 minutes of fast paced sections where it has a more agressive and driving beat. compared to many western pop structures, this arrangement is not foreign to dance music and most genres within this tempo like Drum and bass,techno and acid take from this.
Even looking from the song structure it self, its obvious that it even reflects the whole violent and restless nature of the genre. There is only a 30 seconds interlude, compared to 3 minutes of fast paced sections where it has a more agressive and driving beat. compared to many western pop structures, this arrangement is not foreign to dance music and most genres within this tempo like Drum and bass,techno and acid take from this.
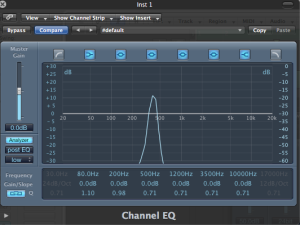
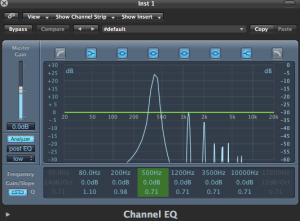
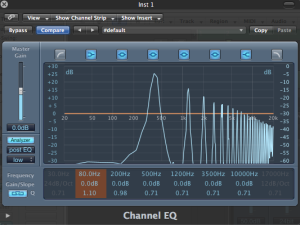
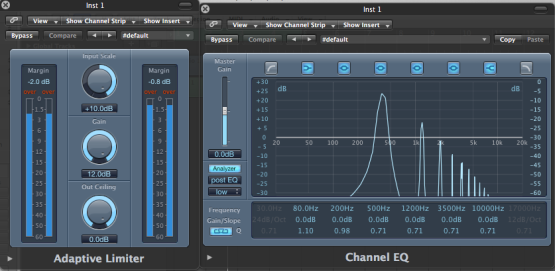
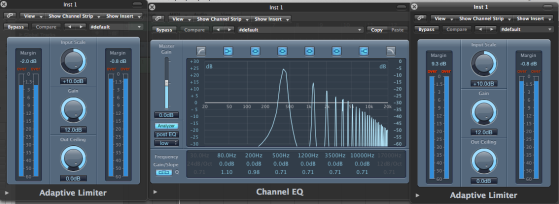
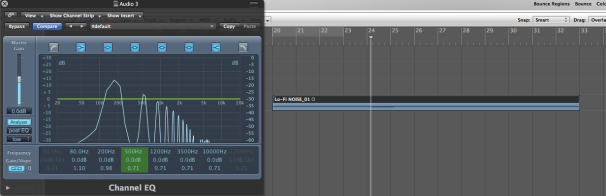
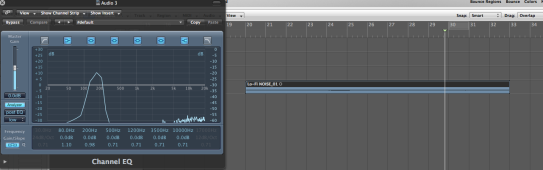
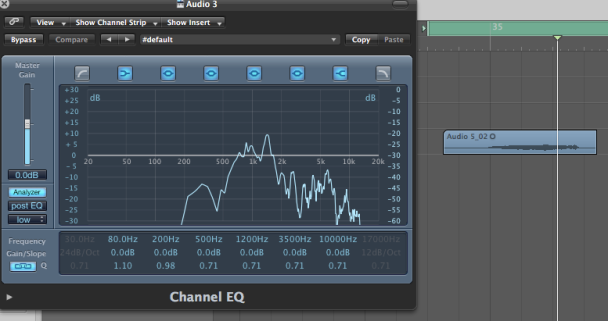
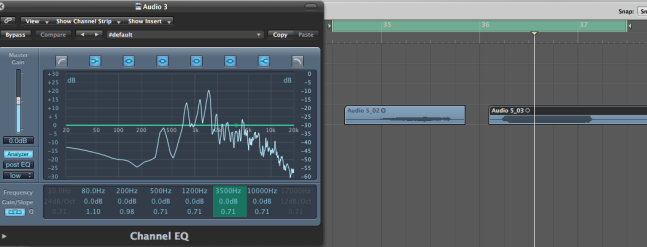









 The general tip i used to be able to identify a certain frequency is to memorise one frequency from the subs,lows,mids and highs and compare it to the next one depending on the relative band it lives in.
The general tip i used to be able to identify a certain frequency is to memorise one frequency from the subs,lows,mids and highs and compare it to the next one depending on the relative band it lives in.